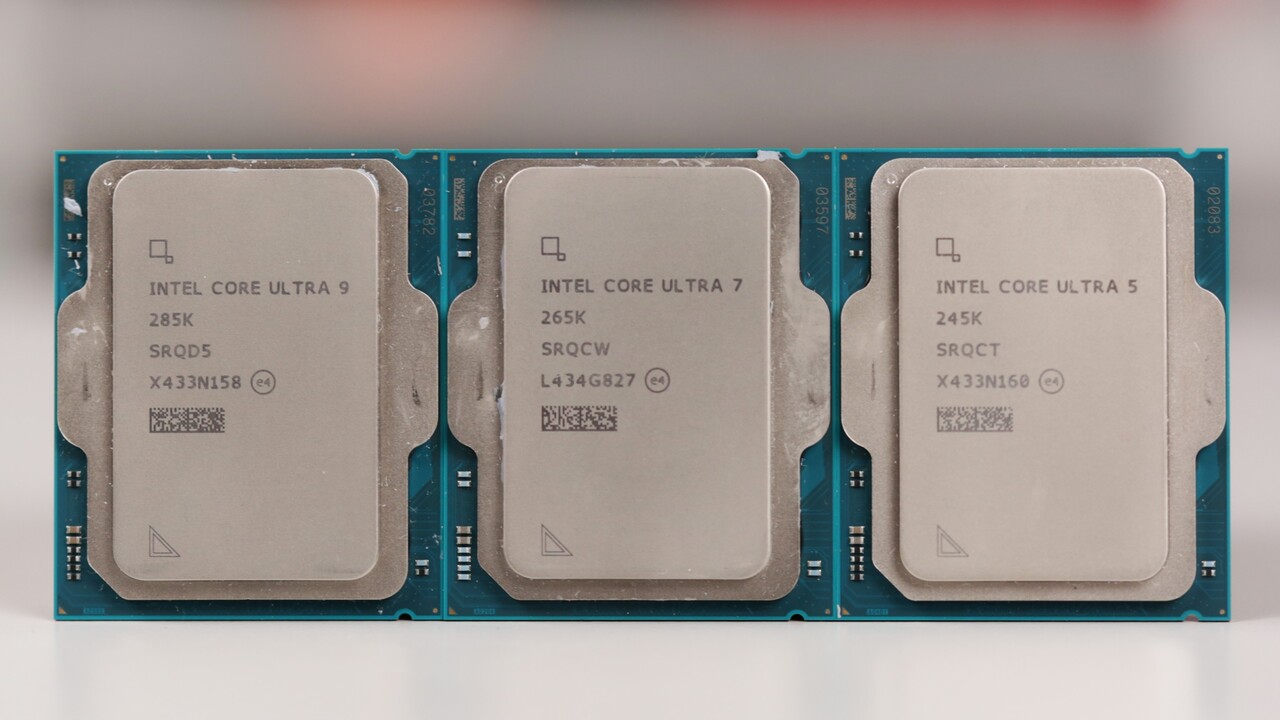
AMD vs. Intel in the XMG NEO 16: Ryzen 9 9955HX vs. Core Ultra 9 275HX from 15 to 180 watts 19 comments

AMD and Intel’s new HX Notebook CPUs are here: desktop processors for mobile use. In the new XMG NEO 16, the Ryzen 9 9955HX and Core Ultra 9 275HX will compete against each other. The “AMD Fire Range” vs. “Intel Arrow Lake-HX” duel isn’t exactly a head-to-head race, but on average, a close one-on-one. Table of Contents 1 Ryzen 9 9955Hx vs. Core Ultra 9 275HX from 15 to 180 Watts AMD HX vs. Intel HX – This is Behind Two XMG NEO 16 as Test Object AMD Fire Range and Intel Arrow Lake HX Overview ~85 Watts Gaming Performance at the CPU Limit Conclusion
AMD HX vs. Intel HX – This is Behind It
Mobile HX processors were launched by Intel with the 12th Core Gen, then adopted in this form by AMD with Ryzen 7000 Mobile: in both cases, these are the largest desktop processors, moving to a BGA package for mobile use. They offer a maximum of as many cores as a Core Ultra 9 285k (test) or a Ryzen 9 9950x (3D) (test), albeit at a lower TDP. However, in some notebooks, they come extremely close to the desktop variants. The scope of application for the two fastest processor series for laptops is clearly defined: they must offer an experience with an additional discrete graphics solution such as a new GeForce RTX 5090 GPU (review) that is equivalent to a classic desktop PC with the advantages of a mobile companion.
Intel Arrow Lake-HX and AMD Fire Range address a market segment that can and should offer a higher power requirement as a base. Arrow Lake-HX benefits from Intel’s know-how in the notebook segment and the new tile architecture, because the old desktop processor can be configured as a classic power-saving notebook solution and then also offers the appropriate performance. With AMD Fire Range it is different, as will be shown.
Two XMG NEO 16 as test object
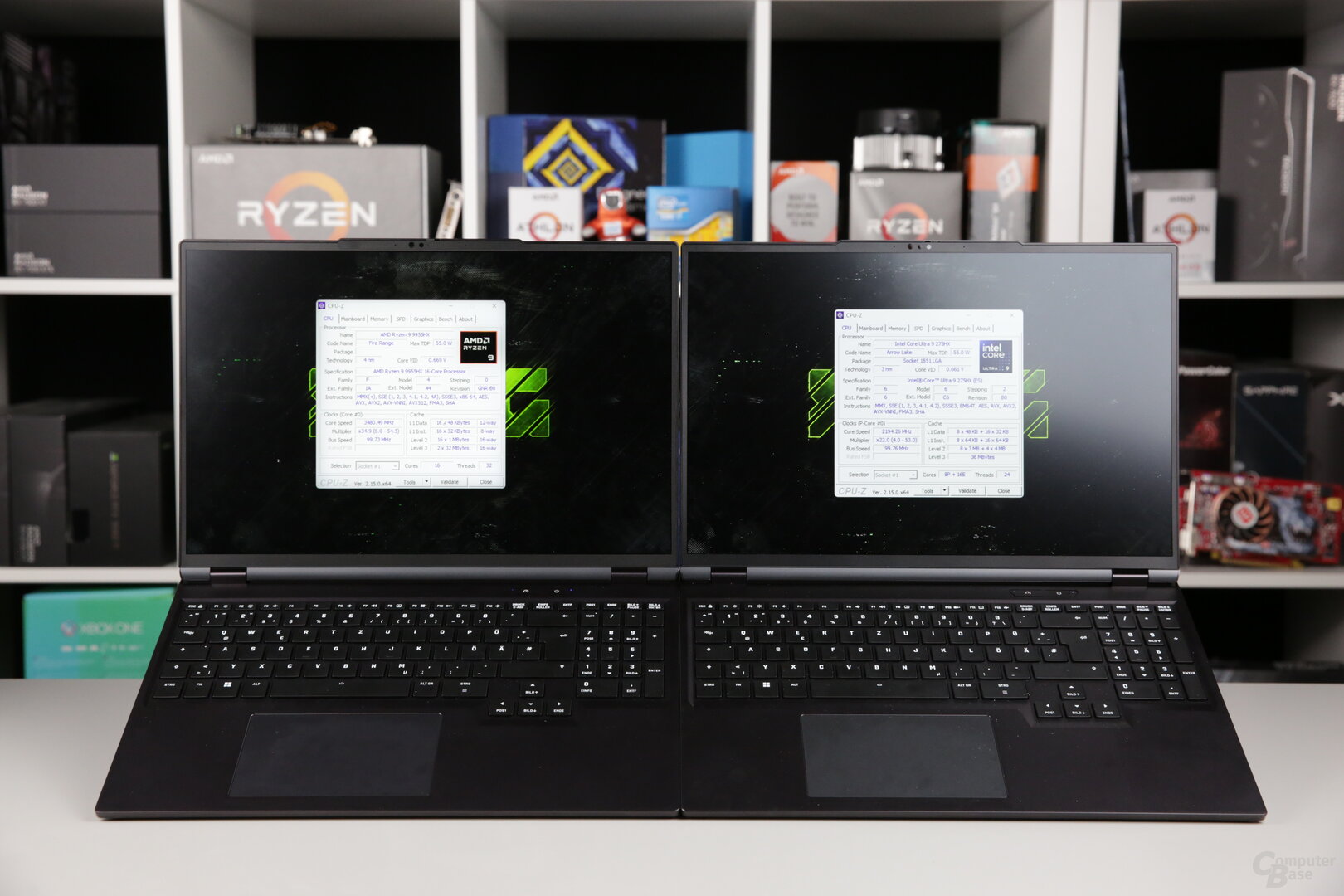
The perfect basis for comparison is the new XMG NEO 16, which is “identical” with Intel Arrow Lake-HX (NEO 16 E25) and AMD Fire Range (NEO 16 A25).
XMG NEO 16: AS A25 with Ryzen 9 9955HX and RTX 5090 Computer GPU
XMG NEO 16: AS A25 with Ryzen 9 9955HX and RTX 5090 Computer GPU
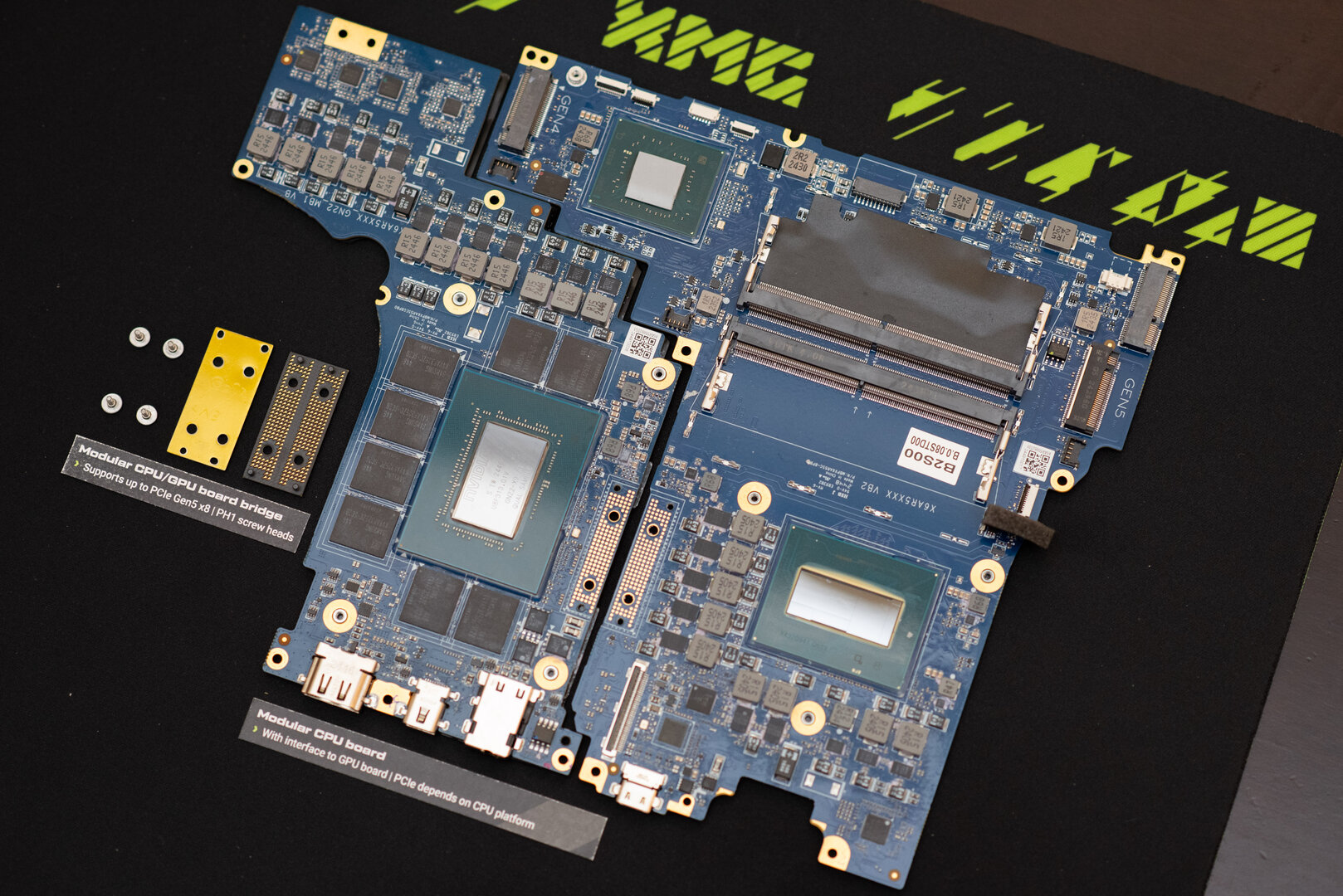
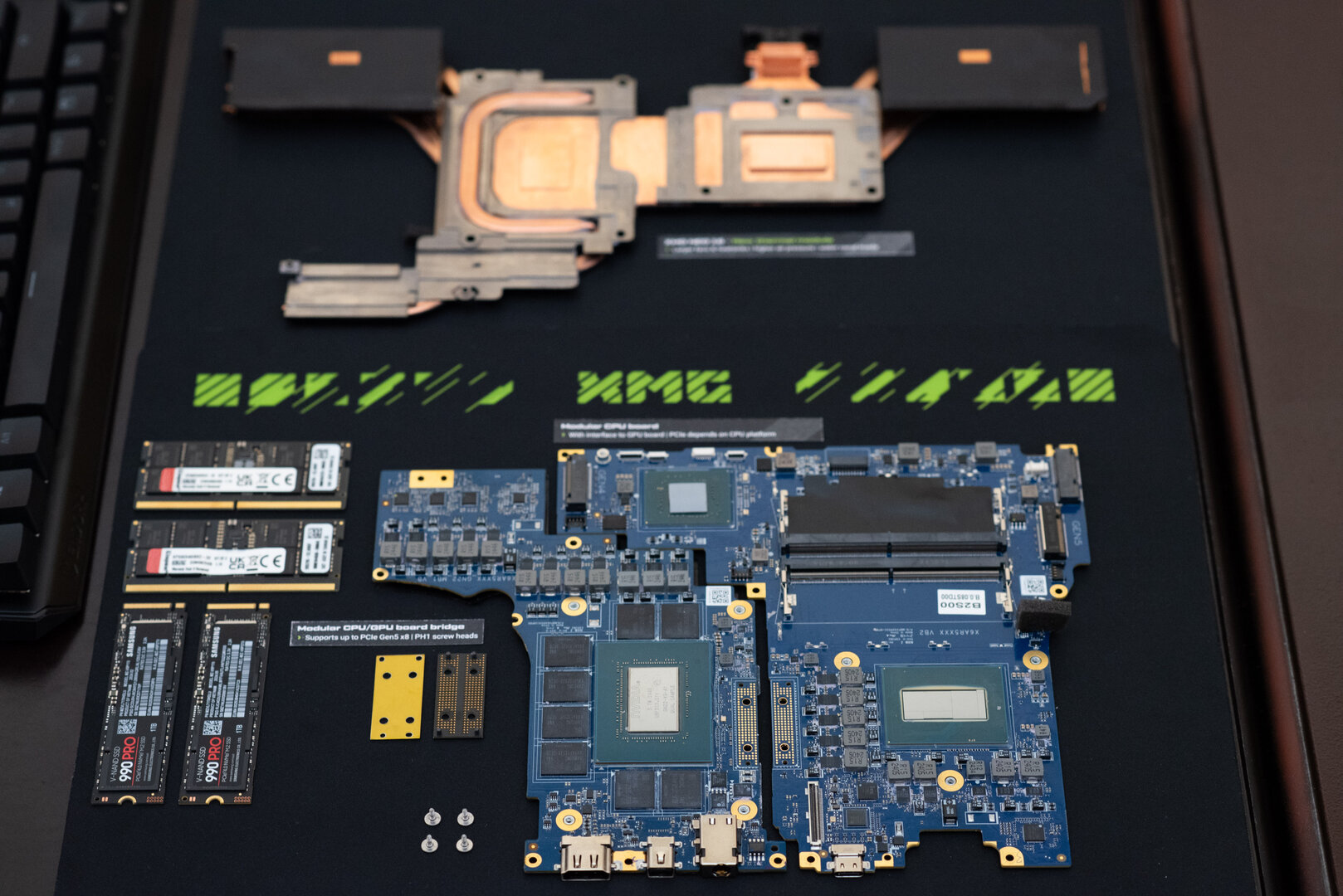
 View of two-part circuit board in XMG NEO 16 (E25)
View of two-part circuit board in XMG NEO 16 (E25)
View of the two-part circuit board in XMG NEO 16 (E25) (image: Schenker XMG)
 The AMD variant also has another CPU selection: in April customers can count on the model with Ryzen 9 9955HX, if you can wait until May you can also order the Ryzen 9 9955HX3D-Quasi A Ryzen 9 9950x3D (test) in BGA format.
The AMD variant also has another CPU selection: in April customers can count on the model with Ryzen 9 9955HX, if you can wait until May you can also order the Ryzen 9 9955HX3D-Quasi A Ryzen 9 9950x3D (test) in BGA format.
XMG NEO 16 (E25) with Core Ultra 9 275HX from 2,699 EUR
CES 2025 XMG NEO 16 inside (12)
CES 2025 XMG NEO 16 inside (12) (image: Schenker XMG)
 Both variants have the well-known XMG control center, with the help of which CPU and GPU can be adjusted in an extremely large volume in terms of maximum recorded performance.
Both variants have the well-known XMG control center, with the help of which CPU and GPU can be adjusted in an extremely large volume in terms of maximum recorded performance.
XMG Control Center allows full adjustments to CPU and GPU TDP
XMG Control Center allows full adjustments to CPU and GPU TDP
 The announcement news provides more details about the new XMG NEO 16 E25 and A25:
The announcement news provides more details about the new XMG NEO 16 E25 and A25:
XMG NEO 16 (E25) and (A25): dual-card, RTX 5000, Core Ultra Oder Ryzen HX (3D)
AMD Fire Range and Intel Arrow Lake-HX Overview
AMD and Intel make it relatively easy with new products. Both take the alias of the Intel Arrow Lake-S and AMD Granite Ridge desktop chip and put it in the notebook on a BGA package to lose. This means that the basic structures and all features are removed, but also the problems of the respective solutions.
AMD Ryzen 9 99550HX and Intel Core Ultra 9 275HX are number 2 in the portfolio. At Intel, there is still the 285hx; Traditionally a “halo chip”, which will rarely be seen on the market. However, this often doesn’t make sense in classic processors, because a disproportionately extra charge has to be paid for the proverbial hundred megahertz, which doesn’t pass the TDP and/or cooling in the notebook anyway.
The Ryzen 9 9955HX3D is different from AMD’s Ryzen 9 9955Hx. It offers one of the CCDs with a stacked L3 cache, which has a positive effect on gaming—if the CCD with the cache also runs off the keyword gaming bar. After all, there were tests for the desktop model of this variant, aka the AMD Ryzen 9 9950x3d, a few days ago. And of course, the GPU limit is lower in the notebook as well: the RTX 5090 laptop GPU is only slightly faster than an RTX 5070 in the desktop PC. Model Codename Kerne /
Threads Basistakt Turbotakt Grafik Grafiktakt L3-CACH TDP AMD Ryzen 9 9955HX3D ZEN 5 (4 nm) 16/32 2.5 GHz 5.4 GHz RDNA 2.2 CUS 2.2 GHz 128 Mbyte 54+ Watt Amd Ryzen 9 9955HX 16/32 2.5 GHz 5.4 Mbyte AMD Ryzen 9 9850Hx 12/24 3.0 GHz 5.2 GHz Intel Core Ultra 9 285Hx ARL-HX (3 nm) 8p + 16e / 24 2.8 GHz 5.5 ghz 4 XE-cores 2 GHz 36 MBE 55+ WATT Intel Core Ultra 9 275Hx 2.7 GHz 5.4 GHz 1.9 GHz CORE ULTRA 7 8p + 12e / 20 2.6 GHz 5.3 GHz 30 mbyte Intel Core Ultra 7 255HX 2.4 GHz 5.2 GHz 1.85 GHz Intel Core Ultra 5 245Hx 6p + 8e / 14 3.1 GHz 5.1 GHz 3 XE-CORES 1.9 GHz 24 mbyte Intel Core Ultra 5 235Hx
Intel has the advantage in memory: Arrow Lake supports DDR5-6400, AMD Fire Range only DDR5-5600 – just like granite rapids in the desktop. The Neo 16 implements both from the factory, but also offers OC profiles in the BIOS. Unlike the AMD platform, all Intel processors also come with a small NPU. With 13 peaks, however, this falls into the “not enough for Copilot+” category. Essentially, this is the Meteor Lake silicon, only slightly higher, and therefore brought from 11 to 13 peaks.
Page 1/2 Next page
Benchmarks and Conclusion Topics: AMD AMD Fire Range Intel Intel Arrow Lake Notebooks Ryzen Processors Schenker XMG Image Image Overview

Marc deciphers processors by testing their performance for gaming, content creation, and artificial intelligence.