GEFORCE RTX 5000 GPUS: Notebook manufacturers must continue to name the TDP 6 comments
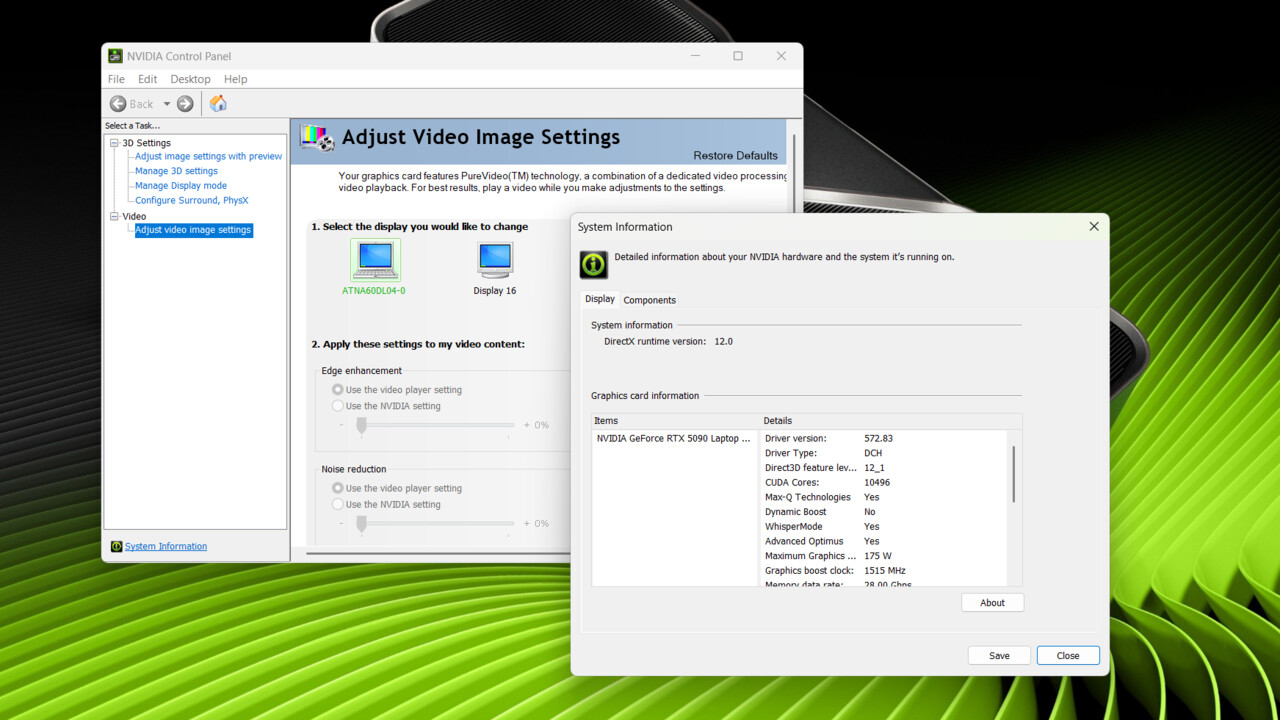
With the NVIDIA GEFORCE RTX 5090 laptop GPU in the Razer Blade 16 (review), the first embargo was tested for Blackwell notebook GPUs today. The GPU operates with a standard TDP of 135 watts plus a maximum of 25 watts via dynamic boost. Razer doesn’t reveal this online. OEMs are still required, Nvidia confirms.
What’s behind it?
Since the GeForce RTX 3000 laptop GPUs, NVIDIA has not been particularly efficient, but also particularly slow variants of a class of mobile graphics cards with the addition of “Max-Q,” which celebrated its 1000th GTX premiere. The computer base had made public that customers are faced with extreme bandwidth from different configurations of “the same” graphics card, whose performance can vary greatly.
Following the ensuing global criticism, Nvidia called on manufacturers to list the maximum allowable TDP of the graphics card and its clock rate on their own homepages.
Does this announcement still apply to the RTX 5000?
Even with the unveiling of the new RTX 5000 laptops for CES 2025 in January, many OEM press releases are now missing this information, but it is also very relevant for the RTX 5000 laptop GPU with a wide TDP range.
When product pages also went live without this information (see Razer, where only the +25 watt dynamic boost is mentioned), Nvidia’s PC base asked what the transparency issue was. NVIDIA shared: As before, work with OEMs to ensure that maximum graphics performance (in watts) is listed on product pages. The announcement continues to apply.
We are working with laptop manufacturers to ensure they list graphics power on their product websites.
For ASUS (e.g., ROG Scar 18), MSI (e.g., Titan 18 HX AI), or XMG (e.g., Neo 16), the information continues to be open, and XMG has already pointed out to the PC base what to do for the smallest configurations in the lowest series.
Manufacturers that currently do not do this should follow suit. Because considering only the maximum allowed power can be used to derive the performance of a GeForce RTX 5000 GPU compared to the same model in another laptop.
The following TDP scaling currently only contains values for RTX 4000 laptop GPUs, but will soon be expanded to include values for the RTX 5090 laptop GPU and another variant.
Problems: Dangase Dangerz RTX 50 NVIDIA GRAPHICS CARDS NVIDIA BLACKWELL

An engineer by training, Alexandre shares his knowledge on GPU performance for gaming and creation.